Keywords: guard rails
- Historical Items (31)
- Tax Records (0)
- Architecture & Landscape (0)
- Online Exhibits (12)
- Site Pages (4)
- My Maine Stories (0)
- Lesson Plans (0)
Online Exhibits
Your results include these online exhibits. You also can view all of the site's exhibits, view a timeline of selected events in Maine History, and learn how to create your own exhibit. See featured exhibits or create your own exhibit
Exhibit
Black soldiers served in Maine during World War II, assigned in small numbers throughout the state to guard Grand Trunk rail lines from a possible German attack. The soldiers, who lived in railroad cars near their posts often interacted with local residents.
Exhibit
A Convenient Soldier: The Black Guards of Maine
The Black Guards were African American Army soldiers, members of the segregated Second Battalion of the 366th Infantry sent to guard the railways of Maine during World War II, from 1941 to 1945. The purpose of the Black Guards' deployment to Maine was to prevent terrorist attacks along the railways, and to keep Maine citizens safe during the war.
Exhibit
For one hundred years, Acadia National Park has captured the American imagination and stood as the most recognizable symbol of Maine’s important natural history and identity. This exhibit highlights Maine Memory content relating to Acadia and Mount Desert Island.
Exhibit
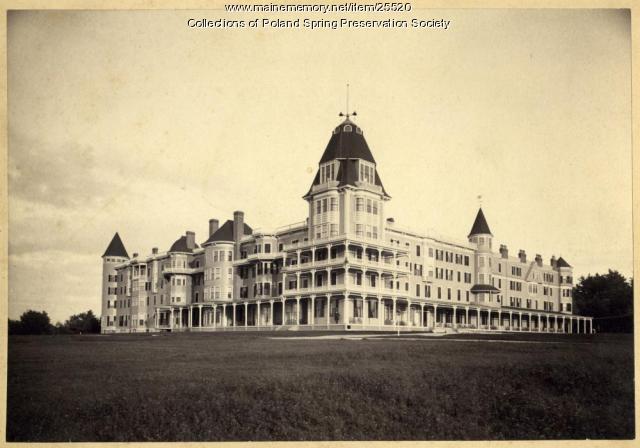
Poland Spring: Summering in Fashion
During the Gilded Age at the end of the nineteenth century, Americans sought to leave increasing urban, industrialized lives for the health and relaxation of the country. The Poland Spring resort, which offered a beautiful setting, healing waters, and many amenities, was one popular destination.
Exhibit
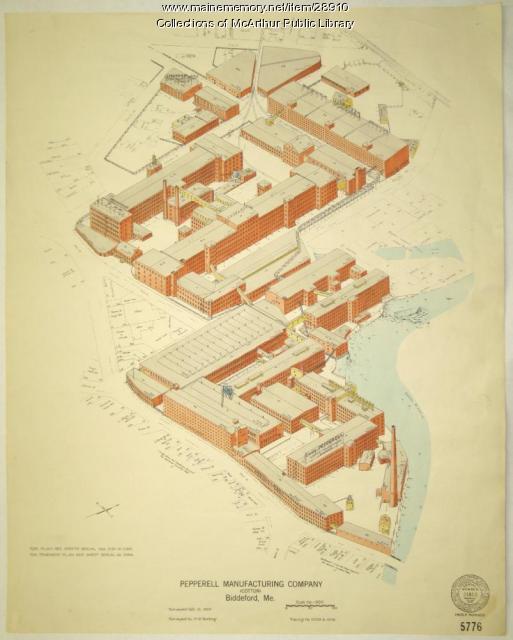
Biddeford, Saco and the Textile Industry
The largest textile factory in the country reached seven stories up on the banks of the Saco River in 1825, ushering in more than a century of making cloth in Biddeford and Saco. Along with the industry came larger populations and commercial, retail, social, and cultural growth.
Exhibit
World War I and the Maine Experience
With a long history of patriotism and service, Maine experienced the war in a truly distinct way. Its individual experiences tell the story of not only what it means to be an American, but what it means to be from Maine during the war to end all wars.
Exhibit
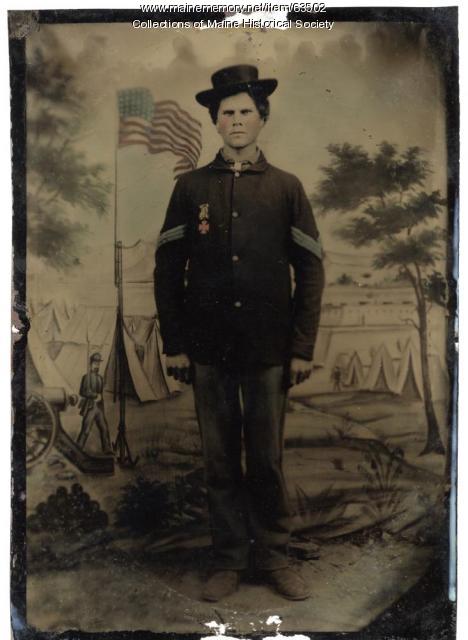
John P. Sheahan, 1st Maine Cavalry, 31st Maine Infantry
John P. Sheahan of Dennysville served in the 1st Maine Cavalry from August 1862 until March 1864 when he was commissioned as a lieutenant in Co. E of the 31st Maine Infantry. His letters reveal much about the life of a soldier, including political views and thoughts about the war.
Exhibit
Maine Eats: the food revolution starts here
From Maine's iconic lobsters, blueberries, potatoes, apples, and maple syrup, to local favorites like poutine, baked beans, red hot dogs, Italian sandwiches, and Whoopie Pies, Maine's identity and economy are inextricably linked to food. Sourcing food, preparing food, and eating food are all part of the heartbeat of Maine's culture and economy. Now, a food revolution is taking us back to our roots in Maine: to the traditional sources, preparation, and pleasures of eating food that have sustained Mainers for millennia.
Exhibit
This Rebellion: Maine and the Civil War
For Mainers like many other people in both the North and the South, the Civil War, which lasted from 1861-1865, had a profound effect on their lives. Letters, artifacts, relics, and other items saved by participants at home and on the battlefield help illuminate the nature of the Civil War experience for Mainers.
Exhibit
Lincoln County through the Eastern Eye
The Penobscot Marine Museum’s photography collections include nearly 50,000 glass plate negatives of images for "real photo" postcards produced by the Eastern Illustrating and Publishing Company of Belfast. This exhibit features postcards from Lincoln County.
Exhibit
Port of Portland's Custom House and Collectors of Customs
The collector of Portland was the key to federal patronage in Maine, though other ports and towns had collectors. Through the 19th century, the revenue was the major source of Federal Government income. As in Colonial times, the person appointed to head the custom House in Casco Bay was almost always a leading community figure, or a well-connected political personage.
Exhibit
The history of the region now known as Maine did not begin at statehood in 1820. What was Maine before it was a state? How did Maine separate from Massachusetts? How has the Maine we experience today been shaped by thousands of years of history?